|
Overview:
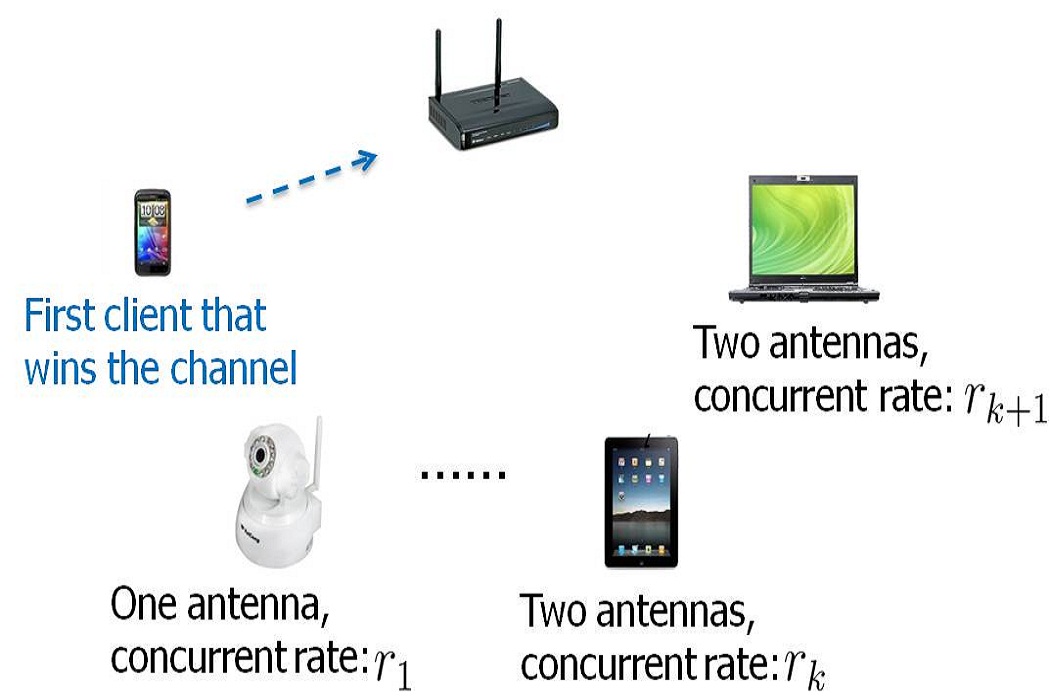
A multiuser-MIMO (MU-MIMO) network contains a multi-antenna access point (AP) and several clients with different (usually one or two) number of antennas. Multiple clients can communicate concurrently with AP in both the uplink (many-to-one) and downlink (one-to-many). With increased spatial reuse, a MU-MIMO network experiences very high network throughput. However, current WLAN is based on CSMA/CA MAC protocol, which allows one client to transmit at a time. Therefore, how to enable multiple clients to transmit concurrently while keeping the random access MAC becomes a hot topic recently. K. Tan et al. [MOBICOM'2009] develops a random access MAC protocol that enables multiple clients to compete for concurrent transmission opportunities. W. L. Shen et al. [MOBICOM'2012] develops a rate adaptation scheme for MU-MIMO WLANs, which allows the client to choose its optimal transmission rate according to who it is transmitting concurrently with.
However, current research on 802.11 MU-MIMO WLANs has not considered the situation when the clients have different number of antennas (usually one or two), and simply assumes that each client has a single antenna. Practically, the number of antennas is limited by the size of the device. For instance, smart phones usually have one antenna, while IPAD has multiple antennas. In a random access MU-MIMO network, where clients have heterogeneous number of antennas, it is possible that a 2-antenna client can only transmit one stream (although AP has multiple antennas). Because different antenna experiences different channel gain, by carefully allocating power and phase in each antenna, the 2-antenna client can obtain the best transmission rate. This is one of the problems that we want to tackle with. On the other hand, since the optimal transmission rate of one client depends on who it is transmitting concurrently with, we can modify the random access protocol by giving clients with larger concurrent transmission rates higher probabilities to win the channel, and thus increase the network throughput. However, this modification will incur unfairness among different clients. This is another problem that we want to address.
People: Shanshan Wu
Papers:
S. Wu, W. Mao, and X. Wang, "Performance Analysis of Random Access Multi-user MIMO Wireless LANs," in IEEE GLOBECOM 2013.
S. Wu, W. Mao, and X. Wang, “Performance Study on a CSMA/CA-Based MAC Protocol for Multi-User MIMO Wireless LANs,” IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 3153-3166, June 2014.
|